Processing Technology of Metal Furniture
 May 08,2025
May 08,2025

 Topmax Furniture
Topmax Furniture
Forming process of metal furniture
1. Cutting Machining
In order to achieve the specified shape, size and surface quality of parts, metal furniture manufacturers need to use cutting tools on cutting machines (or manually) to cut off the excess processing of metal workpieces. This processing method is called Cutting Machining.
According to the processing method, it is divided into turning, milling, planing, grinding, drilling, etc. Materials with high hardness are difficult to cut, but materials with high toughness are also not easy to cut. Cast iron, brass, aluminum alloys, etc. have good cutting properties, while pure copper and stainless steel have poor cutting properties. Through Cutting Machining, you can get the unique texture effect produced by different textures. For example, turning the outer circle of the bar to form a bright surface, shining; the plane milled by the end face produces a spiral halo with a certain trajectory; planing the plane with a planer to form a regular strip texture; scraping the plane can produce twill flowers, fish scale flowers, half-moon flowers and other patterns, and have beautiful reflections.

2. Plastic Working of Metals
Plastic Working of Metals refers to a processing method in which a metal blank undergoes plastic deformation under the action of an external force, thereby obtaining a blank or part with a certain shape, size and mechanical properties. While forming, the material's structure and performance can be improved; the product can be directly produced or easily processed, without cutting and with low metal loss; it is suitable for large-scale production.
(1) Forging
Forging included free forging and die forging. Free forging is a processing method that uses impact force or pressure to cause a metal blank to undergo plastic deformation between an upper and lower grinding wheel (anvil) to obtain a forging of the desired shape, size and internal quality. Die forging is a method in which a metal blank is placed in a forging die cavity with a certain shape, and an impact force or static pressure is applied to cause the metal blank to undergo plastic deformation in the forging die cavity to obtain a forging. Forging has high production efficiency; it can forge forgings with complex shapes, and can make the metal streamlines reasonably distributed, thus improving the service life of parts; die forgings have precise dimensions, good surface quality and small machining allowance; die forgings can reduce the workload of cutting and processing, and can reduce the cost of parts under the condition of sufficient batches; the operation is simple and the labor intensity is low.
(2) Rolling
Rolling is the use of the pressure of two rotating rollers to make the metal billet pass through a specific space to produce plastic deformation, so as to obtain the required cross-sectional shape and change its structural properties at the same time. According to the rolling temperature, it is divided into hot rolling and cold rolling. Cold rolling is the rolling of materials at room temperature. Compared with hot rolling, cold-rolled products have precise dimensions, smooth surfaces and high mechanical strength; cold rolling has high deformation resistance and small deformation, and is suitable for rolling wires and thin plates with good plasticity and small dimensions.
(3) Extrusion process
Extrusion process is the processing method of placing a metal billet in a closed extrusion die and using a strong extrusion force to extrude the metal from the die hole to obtain a billet or part that meets the cross-sectional shape of the die hole. The materials suitable for extrusion processing mainly include low carbon steel, non-ferrous metals and their alloys. Profiles or parts with various cross-sectional shapes can be obtained through extrusion. The commonly used extrusion methods in production are:
Forward extrusion, extrusion in which the metal flow direction is the same as the punch movement direction.
Reverse extrusion, extrusion in which the metal flow direction is opposite to the punch movement direction.
Compound extrusion, extrusion in which the metal flow direction of part of the billet is the same as the punch movement direction, while the metal flow direction of the other part is opposite to the punch movement direction.
Radial extrusion, extrusion in which the metal flow direction is at a 90° angle to the punch movement direction.

(4) Drawing process
Drawing is the process of using tensile force to force a large-section metal billet through the die hole of a certain shape of drawing die to obtain a small-section rough or product with the required cross-sectional shape and size. Drawing production is mainly used to manufacture various wires, thin-walled tubes and various special geometric profiles. The drawn products have high dimensional accuracy, smooth surface and certain mechanical properties. Low carbon steel and most non-ferrous metals and alloys can be drawn.
(5) Stamping process
Stamping process is the processing method in which metal sheets are separated or plastically deformed by being pressed between stamping dies. According to the stamping processing temperature, it is divided into hot stamping and cold stamping. The former is suitable for processing sheets with high deformation resistance and poor plasticity; the latter is carried out at room temperature and is a commonly used stamping method for thin plates. The stamping process is only suitable for processing plastic metal materials. It is powerless for brittle materials such as cast iron and bronze, and is not suitable for processing parts with too complex shapes. For parts with complex shapes and inner cavities, casting is generally more convenient than pressure processing.
When designing stamping parts, metal furniture supplier should pay attention to the fact that the shape of the shape and punching holes should be simple and symmetrical, and regular shapes such as circles and rectangles should be used as much as possible to avoid long grooves and slender arm structures; when punching holes, the diameter of the round hole shall not be less than the entire thickness of the material, the side length of the square hole shall not be less than 0.9 times the thickness of the material, the distance between holes and between holes and sides shall not be less than the thickness of the material, and the protruding or recessed size of the outer edge of the part shall not be less than 1.5 times the thickness of the material.
3. Casting
1) Sand casting
It is a method of casting by making a mold with sand grains. Sand casting has strong adaptability and is almost not limited by the shape, size, weight and type of metal used in the casting. The process equipment is simple, low cost and widely used.
2) Investment casting
It is also called lost wax casting, including wax pressing, wax repairing, tree assembly, slurry dipping, wax melting, casting molten metal and post-processing. Lost wax casting is to make a wax mold of the part to be cast with wax, and then apply mud on the wax mold, which is the mud mold. After the mud mold is dried, it is baked into a ceramic mold. Once baked, the wax mold is completely melted and lost, leaving only the ceramic mold. Generally, a pouring port is left when making the mud mold, and the metal furniture supplier will pour the molten metal from the pouring port. After cooling, the required parts are made.
3) Pressure casting
Die casting for short, on a die casting machine, the metal in the pressure chamber is hydraulically injected into the mold cavity with a high pressure and speed by a pressure piston, and the liquid metal is rapidly solidified into a casting under pressure. It is a precision casting method. The casting has precise dimensions and a smooth surface. It is suitable for the production of small, thin-walled (0.8mm, hole diameter up to 0.8mm, pitch up to 0.75mm) complex castings. The tensile strength of the casting is 25%~40% higher than that of sand casting, and the casting surface can obtain clear patterns, designs and texts. It is mainly used for the production of zinc, aluminum, magnesium, copper and their alloys.
4) Centrifugal casting
The liquid metal is poured into a mold rotating along a vertical or horizontal axis. Under the action of centrifugal force, the metal adheres to the inner wall of the mold and becomes a casting after cooling and solidification. The castings of centrifugal casting have dense structure and good mechanical properties, which can reduce defects such as pores and slag inclusions. It is commonly used to manufacture tubular or hollow cylindrical castings of various metals, and can also manufacture castings of other shapes.
5) Metal mold casting
The method of pouring liquid metal into a metal mold under gravity to obtain a casting.

4. Welding processing
Welding processing is a process that uses the characteristics of metal materials that are easy to melt under high temperature to connect metals to each other. Commonly used welding methods include fusion welding, pressure welding, brazing, etc. Welding processing saves materials and has a light structure; it can be assembled from small to large to manufacture heavy and complex machine parts; the joints not only have good mechanical properties, but also have good sealing.
5. Powder metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is a process method that uses metal powder or metal compound powder as raw material, and obtains materials or products of desired shape and performance through mixing, forming and sintering. Commonly used metal powders include iron, copper, platinum, aluminum, nickel, tungsten, chromium and titanium powders, and alloy powders include nickel bronze, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, high temperature alloy, low alloy steel and stainless steel. Powder metallurgy can produce products that cannot or are difficult to produce using traditional smelting or processing methods.
Production process of metal furniture
Different metal furniture has different manufacturing processes. Some metal furniture also uses materials such as wood, soft materials, plastics and glass. According to the design requirements of metal furniture manufacturers, choose appropriate processes to process various materials. The processing process of the metal part is roughly shown in the figure.
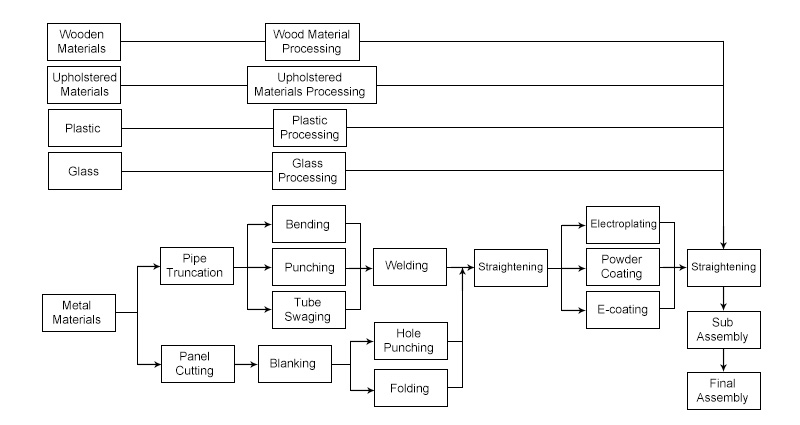
Production process of metal furniture
1. Pipe Truncation or Panel Cutting
Metal substrates are generally large or long, so they need to be cut first to make them smaller for further processing. Gas cutting, grinding wheel cutting, laser cutting and other methods are commonly used. Milling and other methods can also be used for cutting.
2. Bending
Panel bending can be done by stamping; while pipe bending requires bending the material into an arc shape using a profile wheel on a special machine tool. Bending pipes can generally be divided into two processing methods: hot bending and cold bending. Hot bending is used for thick or solid pipes and is less used in metal furniture. Cold bending is bending at temperature and pressurized. The pressurization methods include mechanical pressurization, hydraulic pressurization and manual pressurization. Bending pipes are often used to make the skeleton structure of furniture.
3. Punching
Punching can be done by punching, which has high processing accuracy and high efficiency; drilling can be done by drilling machines and hand drills. If slots are used in the design, milling can be used.
4. Welding
The welding of metal furniture parts often uses gas welding, arc welding and other methods. After welding, the welding points need to be polished to make the surface smooth to avoid affecting the appearance.
5. Surface treatment
There are many surface treatment processes for metals. Metal furniture manufacturers can use chemical coloring, electrolytic coloring, anodizing coloring, plating coloring, coating coloring, enamel coloring, heat treatment coloring and other methods to improve the aesthetics of metal furniture and protect the surface of metal materials from oxidation.
6. Assembly
Metal furniture supplier can assemble metal parts into furniture using screws, bolts, rivets, etc. according to different connection methods.
 Inquire Now
Inquire Now



 Home
Home Rattan Furniture Manufacturing Process in China
Rattan Furniture Manufacturing Process in China  You May Also Like
You May Also Like 





















 Tel
Tel  Email
Email  ADDRESS
ADDRESS 














